Paragon AI Framework
GPU-agnostic, cross-platform AI runtime built in Go with WebGPU acceleration. Designed for deterministic reproducibility and true portability across CPU, GPU, browser, and embedded systems.
"One model, any device."
Portal (WASM)
Isomorphic WASM loader for running Paragon in browsers and Node.js. Same API across all JavaScript environments with zero conversion overhead.
Teleport (C-ABI)
Language-agnostic C ABI wrapper enabling native integration across C, C++, Rust, Python, and more. Dynamic JSON-based method invocation with CPU/GPU switching.
Paragon-Py
Official Python bindings via ctypes. Cross-vendor GPU acceleration with Vulkan, Metal, DirectX, and OpenGL backends. Pure Python, no build step required.
Framework Capabilities
Reproducibility Demo: MNIST Classification
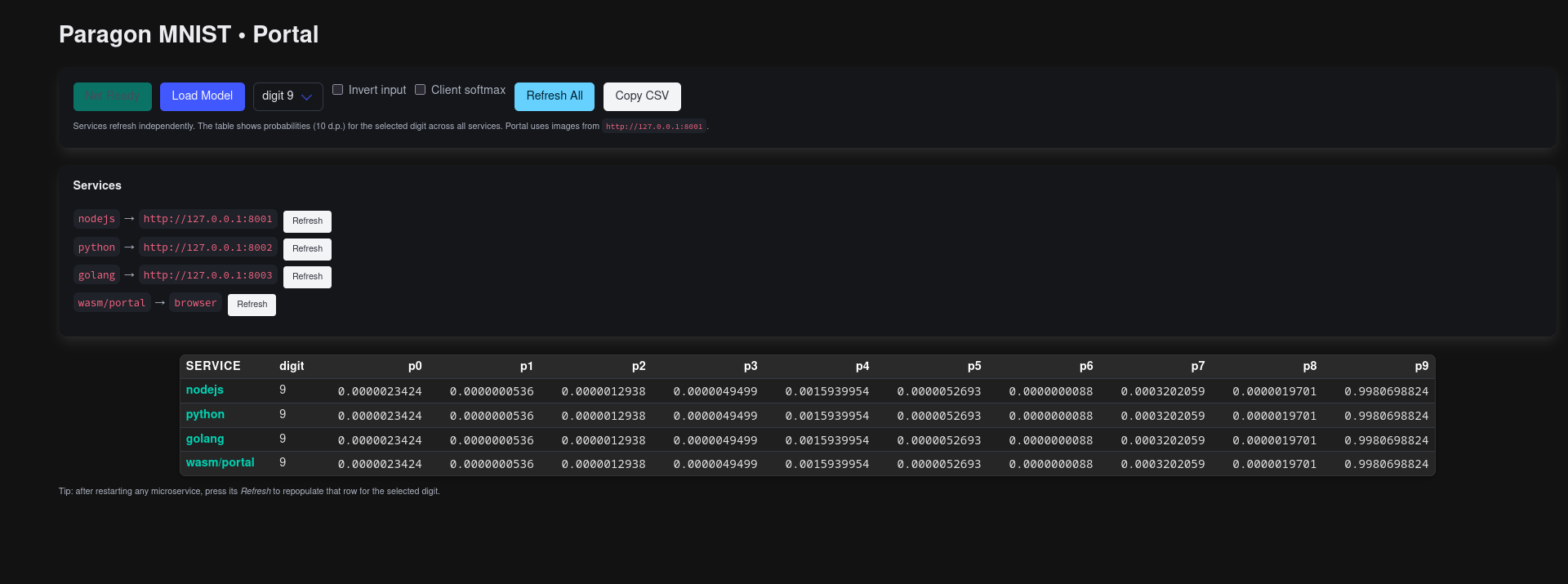
Identical MNIST inference results across Node.js (Teleport), Python (paragon-py), Go (native), and Browser (Portal/WASM) — demonstrating true cross-platform reproducibility without model conversion.
Key Features
Cross-Platform Consistency
Same model, same weights, identical outputs across browser, server, desktop, and mobile. No conversions, no drift.
GPU Acceleration
WebGPU-powered inference on NVIDIA, AMD, Intel, Apple, and Qualcomm GPUs. Automatic CPU fallback when needed.
Language Agnostic
Use from JavaScript, Python, C, C++, Rust, or any language with FFI support. One framework, any language.
Deterministic Training
Reproducible results across devices and platforms. Essential for AI research, benchmarking, and debugging.
Start Building with Paragon
Explore the documentation, try the examples, and join the community building the future of portable AI.
Quick Start Examples
import { initPortal } from "@openfluke/portal";
const main = async () => {
console.log("⚙️ initPortal()…");
const portal = await initPortal();
const config = {
name: "Alpha",
layers: [
{ Width: 1, Height: 1 },
{ Width: 2, Height: 1 },
{ Width: 3, Height: 1 }
],
activations: ["linear", "relu", "softmax"],
};
const nn = portal.NewNetworkFloat32(
JSON.stringify(config.layers),
JSON.stringify(config.activations),
JSON.stringify([true, true, true])
);
nn.PerturbWeights(JSON.stringify([0.1, Date.now() % 1000]));
const input = JSON.stringify([[[Math.random()]]]);
nn.Forward(input);
console.log(config.name, "→", nn.ExtractOutput());
};
main();import paragon_py as paragon
# Create a small 3-layer network
h = paragon.new_network(
shapes=[(4, 8), (8, 8), (8, 2)], # width x height per layer
activations=["relu", "relu", "relu"],
trainable=[True, True, True],
use_gpu=True
)
# Initialize GPU backend (optional but faster)
paragon.initialize_gpu(h)
# Forward pass
sample_input = [[0.1, 0.5, 0.3, 0.7]]
paragon.forward(h, sample_input)
# Extract output
out = paragon.extract_output(h)
print("Network output:", out)
# Cleanup GPU resources
paragon.cleanup_gpu(h)
go get github.com/openfluke/paragon/v3
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/openfluke/paragon/v3"
)
func main() {
// Load MNIST data
trainInputs, trainTargets, _ := loadMNISTData("mnist_data", true)
testInputs, testTargets, _ := loadMNISTData("mnist_data", false)
// Define network: 28x28 input, 16x16 hidden, 10x1 output
layers := []struct{ Width, Height int }{
{28, 28}, {16, 16}, {10, 1},
}
acts := []string{"leaky_relu", "leaky_relu", "softmax"}
full := []bool{true, false, true}
nn := paragon.NewNetwork[float32](layers, acts, full)
// Enable WebGPU acceleration
nn.WebGPUNative = true
err := nn.InitializeOptimizedGPU()
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("Failed to initialize WebGPU: %v\n", err)
return
}
defer nn.CleanupOptimizedGPU()
// Train
nn.Train(trainInputs, trainTargets, 5, 0.01, true, 5, -5)
// Evaluate
var expected, predicted []float64
for i := range testInputs {
nn.Forward(testInputs[i])
nn.ApplySoftmax()
out := nn.GetOutput()
predicted = append(predicted, float64(paragon.ArgMax(out)))
expected = append(expected, float64(paragon.ArgMax(testTargets[i][0])))
}
nn.EvaluateModel(expected, predicted)
fmt.Printf("ADHD Score: %.2f\n", nn.Performance.Score)
}
git clone https://github.com/openfluke/teleport
Teleport is the C-ABI bridge to Paragon. Build the shared library first, then link against it from C, C++, Rust, or any FFI-compatible language.
// Build Teleport shared library:
// go build -buildmode=c-shared -o libteleport.so
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "teleport.h" // Generated header from Teleport
// Helper to parse handle from JSON response
static long long parse_handle(const char* js) {
const char* h = strstr(js, "\"handle\"");
if (!h) return 0;
const char* colon = strchr(h, ':');
while (colon && (*++colon==' '||*colon=='\t'));
return (long long)strtoll(colon, NULL, 10);
}
int main(void) {
// Define network architecture
const char* layers =
"[{\"Width\":784,\"Height\":1},"
"{\"Width\":256,\"Height\":1},"
"{\"Width\":10,\"Height\":1}]";
const char* activ = "[\"relu\",\"relu\",\"softmax\"]";
const char* fully = "[true,true,true]";
// Create network via Teleport
char* r = Paragon_NewNetworkFloat32(layers, activ, fully, true, false);
printf("NewNetwork → %s\n", r);
long long h = parse_handle(r);
Paragon_FreeCString(r);
// Initialize weights
r = Paragon_PerturbWeights(h, 0.1, 42);
Paragon_FreeCString(r);
// Enable GPU acceleration
r = Paragon_EnableGPU(h);
printf("EnableGPU → %s\n", r);
Paragon_FreeCString(r);
// Forward pass with dummy input
char* input = "[[[0.1,0.2,0.3,...]]]"; // 784 values
r = Paragon_Call(h, "Forward", input);
Paragon_FreeCString(r);
// Extract output
r = Paragon_Call(h, "ExtractOutput", "[]");
printf("Output: %s\n", r);
Paragon_FreeCString(r);
// Cleanup
Paragon_Free(h);
return 0;
}
// Compile:
// gcc -o mnist mnist.c -L. -lteleport -Wl,-rpath,'$ORIGIN'